Optical Bonding
Blaze Display Technology Co., Ltd. | Updated: Nov 27, 2018
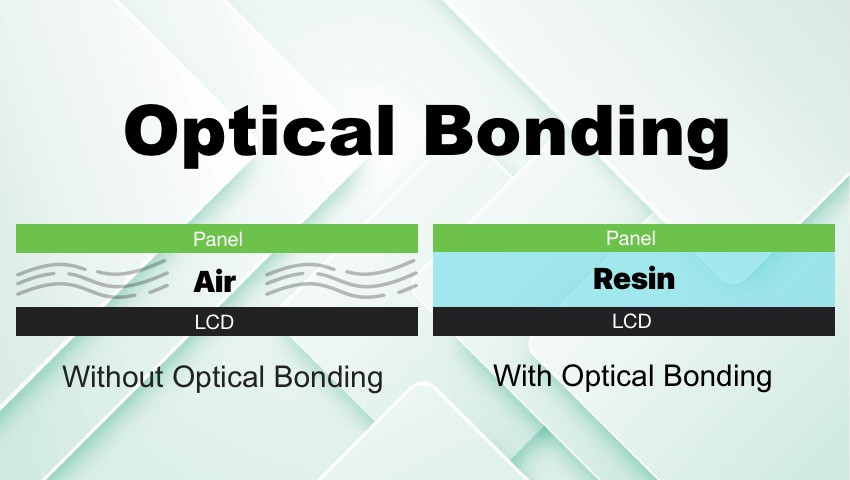
Many applications, particularly in harsh environments, require specific modifications to their electronic displays to improve durability and visibility while reducing glare and condensation. One way to enhance all of these aspects is by adding optical bonding.
What is Optical Bonding?
Optical bonding is the process of directly adhering a protective glass or plastic cover to a display screen, such as an LCD or OLED panel, using a special adhesive layer. This adhesive layer, which is typically made of silicon, epoxy, or urethane, replaces the usual air gap that exists between the display and the cover glass.
Optical bonding enhances display durability and visibility while reducing glare and condensation, particularly in outdoor settings where moisture, wind, sunlight, and other factors can impact display performance.
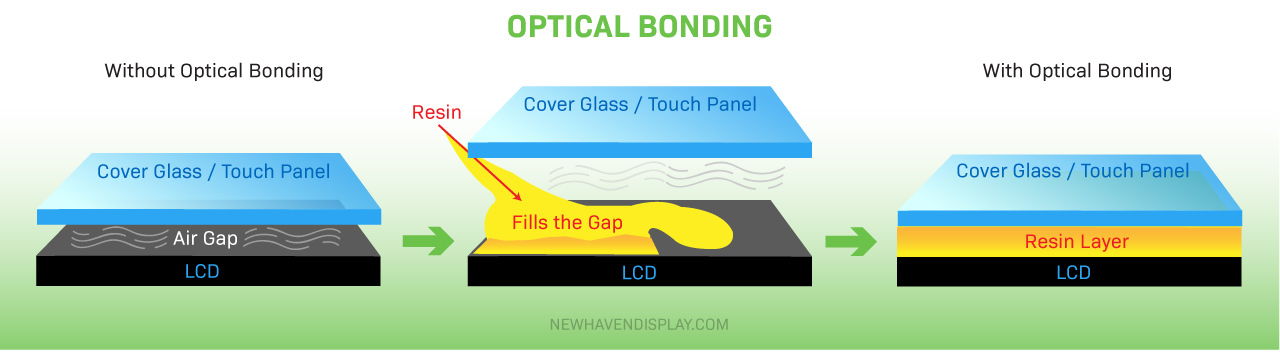
Types of Optical Bonding
There are two types of optical bonding: wet bonding and dry bonding.
- Wet Bonding: Uses a liquid optically clear resin (OCR), also known as LOCA (Liquid Optical Clear Adhesive), that fills gaps and cures into a solid.
- Dry Bonding: Uses pre-formed, solid, optically clear adhesive (OCA) to create a durable bond. There are two main variations in dry bonding:
- Traditional Dry Bonding: This method utilizes heat and pressure to activate the adhesive, which is generally faster and more cost-effective than wet bonding, but might struggle with uneven surfaces.
- UV-Cured Dry Bonding: UV-cured dry bonding involves using a pre-cut sheet of adhesive known as self-clear adhesive (SCA) or UV-OCA, which hardens through exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light.
Materials Used for Optical Bonding
There are different adhesive types available, and the one you select will depend on your specific requirements and application needs. The most common optical bonding adhesive types are:
- Silicon: Silicon is widely used as an adhesive because it is flexible, can withstand high temperatures, and can absorb shocks and vibrations. It also has good optical transparency and doesn't turn yellow over time, which helps to maintain the display's visual clarity. However, when rubbed, silicon can produce debris around the edges, making edge protection necessary in applications such as touchscreens.
- Epoxy: Epoxy Offers better heat resistance and a stronger bond than silicon, making it ideal for high-precision and structural applications. However, once bonded, it is not reworkable. It also requires a careful application due to its fast curing time.
- Acrylic: This material is suitable for rapid production processes as it is UV-curable. However, it might have lower heat resistance than other options and can shrink slightly during curing, requiring precise application.
- Polyurethane: Polyurethane adhesives can endure extreme conditions but are more expensive than other options like silicone and epoxy. They tend to turn yellow over time when exposed to light.
Optical Bonding Application Process
- Preparation: The display panel and the cover glass are thoroughly cleaned to remove dust and other particles.
- Application of Adhesive: A layer of dry or liquid adhesive is applied on the display panel or the inside surface of the cover glass.
- Bonding: The cover glass is carefully aligned and placed on the display panel, and the adhesive is cured using UV light or heat, forming a solid bond.
- Inspection: The bonded display is inspected for quality, ensuring no bubbles or misalignments.
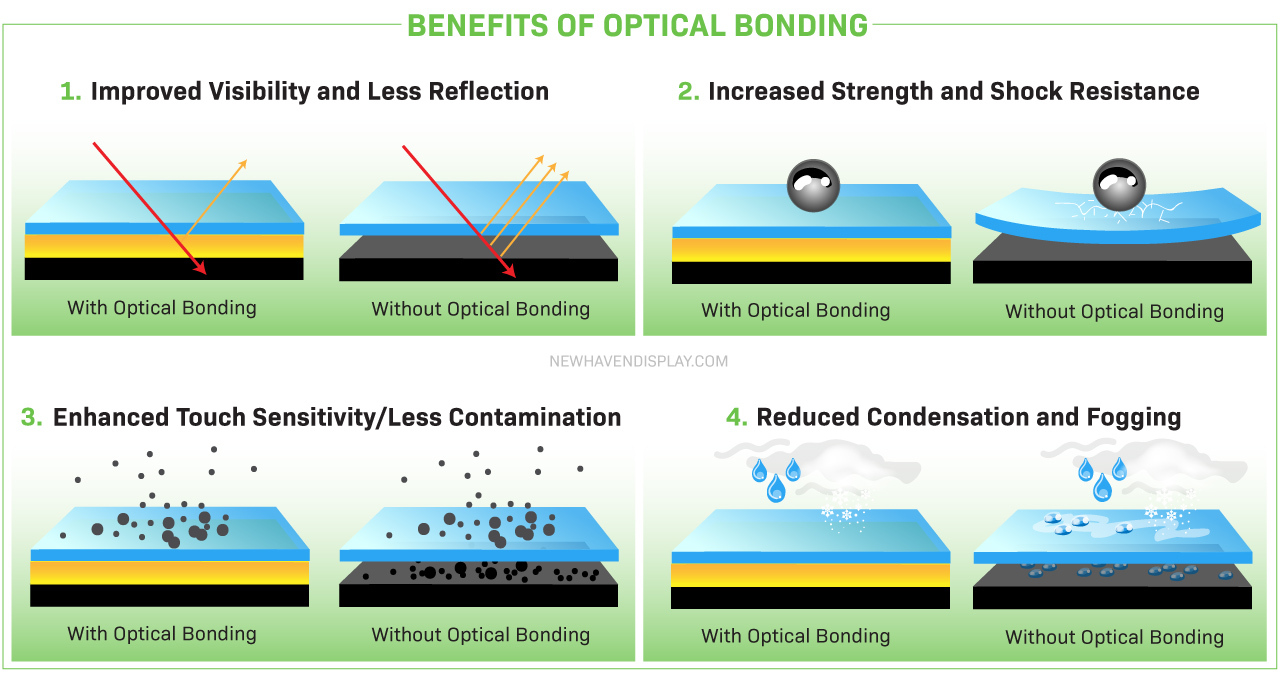
Benefits of Optical Bonding
- Improved visibility and less reflection: Optical bonding eliminates the air gap, which reduces light reflection and refraction. This leads to a significant decrease in glare and enhances the readability of the display in various lighting conditions.
- Increased strength and shock resistance: The bonded layer adds structural strength to the display, which makes it more resistant to shocks, vibrations, moisture, and dust. This means that the display can withstand harsh environments without getting damaged.
- Enhanced touch sensitivity/less contamination: For touchscreen displays, optical bonding improves the sensitivity and accuracy of the touch interface, providing a smoother user experience.
- Reduced condensation and fogging: In environments with fluctuating temperatures, optical bonding prevents condensation and fogging within the display.
Applications of Optical Bonding
Optical bonding enhances display performance, visibility, and durability in harsh environments and extreme temperatures. Here are some of the most common applications of optical bonding:
- Consumer electronics: Optical bonding is widely used in portable devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops to improve display readability and durability.
- Automotive displays: Optical bonding is essential for car dashboards, instrument clusters, and infotainment systems, as it can withstand extreme temperatures.
- Medical devices: Optical bonding is used in medical displays for diagnostic equipment, surgical monitors, and patient monitoring systems to improve visibility and reduce the risk of contamination.
- Industrial displays: Optical bonding is used in industrial automation equipment, human-machine interfaces (HMIs), and other rugged applications.
- Outdoor displays: Optical bonding is used in digital signage, kiosks, and other outdoor displays to improve readability in bright sunlight and increase durability, even in harsh weather conditions.
- Military and aerospace displays: Optical bonding is used in military and aerospace displays to enhance durability and reliability in harsh conditions.
Conclusion
Optical bonding is an effective solution to enhance display screens' clarity, durability, and functionality. This technique is used across multiple industries and applications, and the adhesive materials and bonding process type will depend on each application's unique requirements and environment.

